This blog explains the basic requirements of CMMC, the latest timeline, projected costs of compliance, and tips on how to get started on CMMC compliance.
What is CMMC Compliance?
CMMC (Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification) was introduced by the Department of Defense (DoD) to address widespread gaps in compliance and enforcement of the existing NIST SP 800-171 framework. While CMMC doesn’t introduce new cybersecurity requirements for protecting FCI (Federal Contract Information) and CUI (Controlled Unclassified Information), it strengthens enforcement of the measures already in place.
Previously, defense contractors were allowed to self-assess their compliance with DoD security requirements. Under CMMC, however, most contractors will need to undergo independent third-party assessments to verify compliance. These assessments will be conducted by CMMC Third Party Assessment Organizations (C3PAOs) that are trained and certified by the Cyber AB, CMMC’s official accreditation body.
Matt Travis, CEO of Cyber AB, put it simply – “CMMC is you proving to the Department of War that you are a worthy business partner”.
Who Needs CMMC Certification?
Organizations that handle FCI or CUI must achieve CMMC certification at the level specified in their contract. This requirement applies not only to large, Prime defense contractors but also to subcontractors and smaller organizations further down the Defense Industrial Base (DIB) supply chain. Cybercriminals often target these smaller entities, viewing them as less secure entry points to sensitive data. By raising cybersecurity standards across the entire supply chain, the DoD aims to mitigate these vulnerabilities, which is the core objective of the CMMC program.
CMMC Levels Explained
There are three levels of CMMC compliance that are determined by the type of information your organization handles. To work on defense contracts, your organization must comply with the CMMC level specified in your contract and undergo the appropriate assessments, as shown in the figure below.
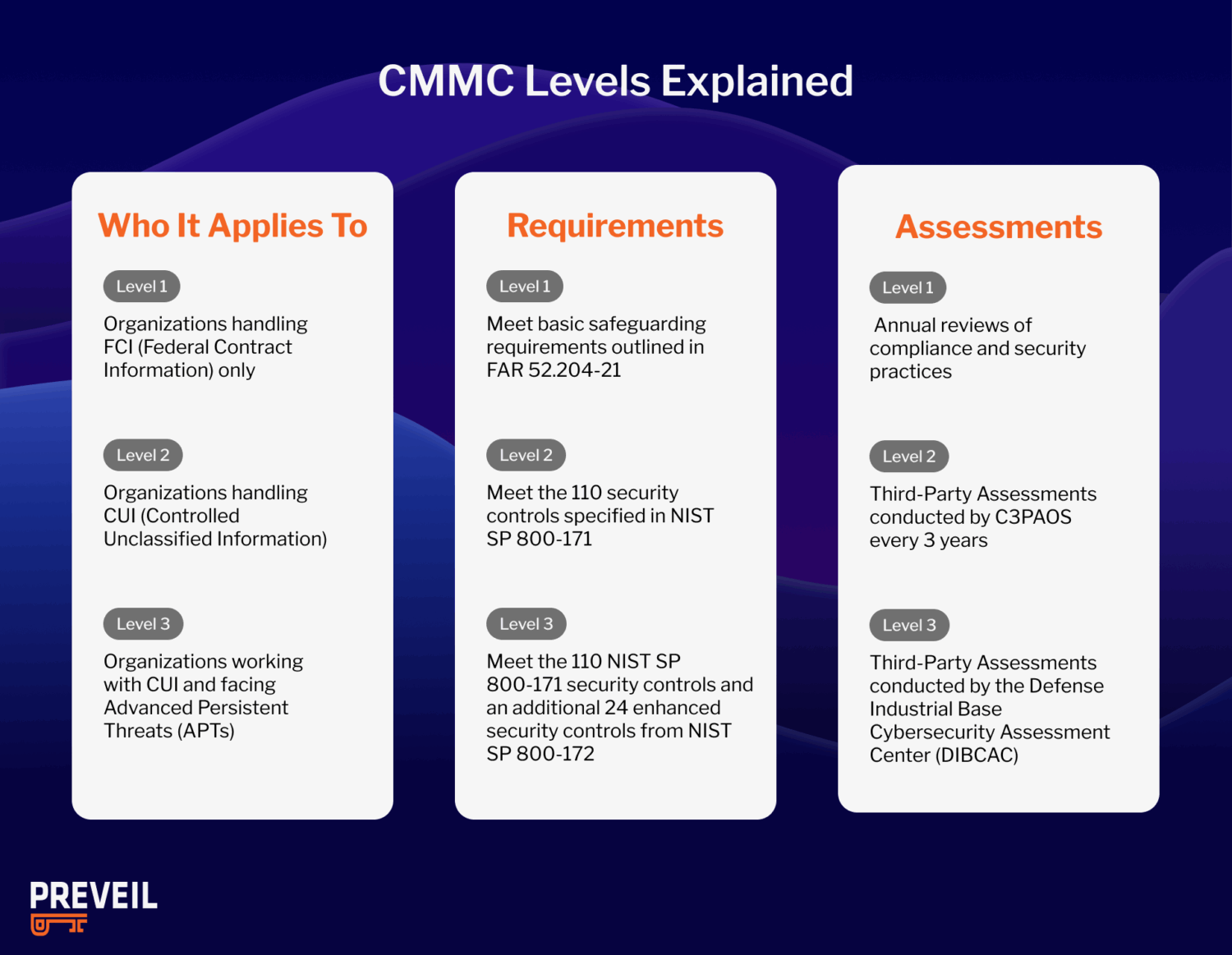
- CMMC Level 1 requirements apply to organizations handling Federal Contract Information (FCI) only. Compliance requires meeting the basic safeguarding requirements outlined in FAR 52.204-21. Organizations at this level must perform annual self-assessments to verify compliance.
- CMMC Level 2 requirements are designed for organizations that handle CUI. Compliance at this level involves meeting the 110 security controls specified in NIST SP 800-171. Most organizations at this level will need to undergo third-party assessments every three years. These assessments are conducted by accredited CMMC Third Party Assessment Organizations (C3PAOs), who evaluate compliance with NIST SP 800-171 controls..
- CMMC Level 3 requirements apply to organizations working with CUI and facing Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), which are sophisticated, state-sponsored attacks targeting critical defense programs. To achieve Level 3, organizations must comply with both the 110 NIST SP 800-171 security controls and an additional 24 enhanced security controls from NIST SP 800-172. Triennial assessments at this level are conducted by the Defense Industrial Base Cybersecurity Assessment Center (DIBCAC), the DoD’s ultimate authority on compliance.
CMMC Compliance Requirements
Once you’ve determined your CMMC level, you will need to meet a defined set of security requirements based on the sensitivity of the data they handle. Below are the core CMMC compliance requirements organizations should understand:
- Access Control: Limit system access to authorized users, processes, and devices. In CMMC Level 2, you must meet the 100 controls outlined in NIST SP 800-171.
- Identification & Authentication: Verify user identities before granting access to systems or data.
- Encryption & Cryptography: Use FIPS 140-2 validated cryptographic modules when encrypting CUI.
- Incident Response: Establish and test plans for detecting, reporting, and recovering from cyber incidents. These are outlined in DFARS 252.204-7012 (c)–(g).
- Configuration Management: Implement and maintain secure system configurations and document changes.
- Audit & Accountability: Create logs, monitor system activity, and retain audit records for review.
- System & Communications Protection: Protect information during transmission and safeguard network boundaries.
- Personnel Security: Screen employees and ensure access is revoked promptly when roles change.
- Risk Assessment: Conduct regular evaluations of system vulnerabilities and implement remediation plans.
- Security Awareness & Training: Provide ongoing cybersecurity training to all users with system access.
- Maintenance & Media Protection: Control access to system maintenance and secure data storage, transfer, and disposal.
- Documentation & Scope: For CMMC Level 2, companies will need to maintain an SSP, SOPs, POA&M, Customer Responsibility Matrix, and artifacts and limit CUI scope (for example, via a secure enclave).
Learn more about achieving CMMC compliance below:
When Will CMMC Be Required?
CMMC is now live and CMMC requirements are now in contracts. See our CMMC timeline blog for more details.
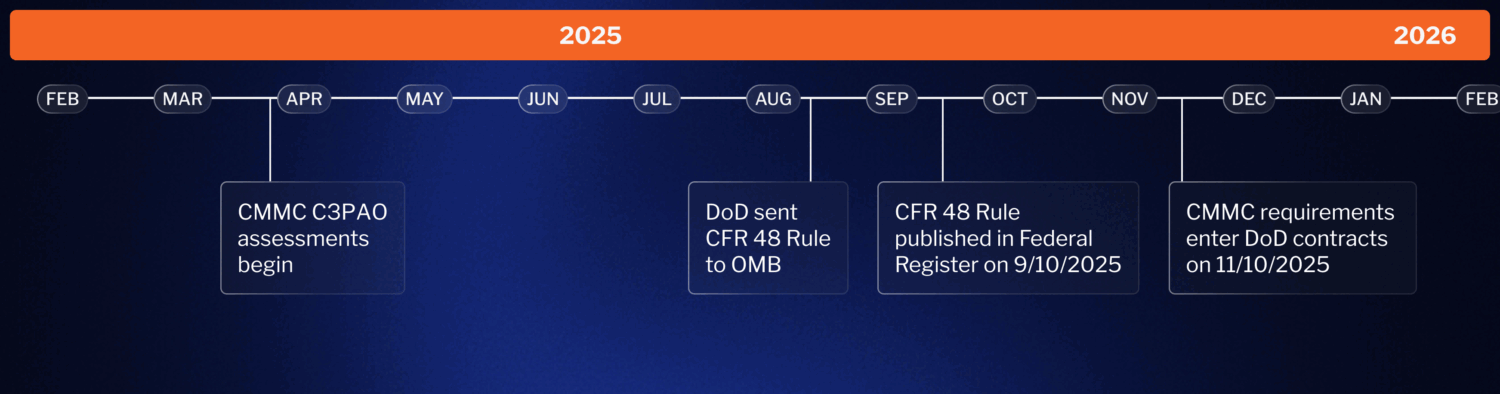
It is important to understand that even though CMMC will be phased in over time, it does not necessarily follow that you have more time to achieve CMMC certification. Your organization, for example, could be far down the supply chain from a contractor subject to CMMC in Phase 1, in which case that contractor must flow down CMMC requirements to your organization at that time.
As leading cyber lawyer Robert Metzger said during PreVeil’s CMMC Summit:
The problem for most contractors is that you won’t know in advance when the compliance requirement will come to you or when your Prime will ask you to show you are ready for a certification assessment. Most organizations find that it takes 6-18 months to know that you are ready to pass an assessment. So you need to get started now.
How Much Does CMMC Certification Cost
The DoD estimates that small defense contractors will need to spend over $100K to achieve CMMC Level 2 with a C3PAO assessment, and submit annual affirmations of compliance, as shown below.
DoD CMMC Level 2 Certification and Cost Estimates
Per the DoD for small defense contracts with less than 500 employees or revenue under $7.5 Million, these are the estimated costs associated with CMMC certification by phase.
- To conduct the CMMC assessment the estimated cost is $76,743.
- To plan and prepare for the C3PAO assessment the estimated cost is $20,699.
- To report CMMC assessment results the estimated cost is $2,851.
- And the annual affirmations will cost an estimated $1,459 each year, which over a 3 year period will come to $4,377.
In total, the costs of a CMMC certification comes to an estimated $104,670.
These CMMC certification cost estimates include time spent by both in-house IT specialists and External Service Providers (ESPs) such as Registered Practitioners (RPs), Certified CMMC Assessors (CCAs), and C3PAOs.
These cost estimates start at the C3PAO assessment phase and do not include any costs up to that point. That’s because defense contractors have been required to comply with NIST SP 800-171, which CMMC Level 2 requirements mirror, since 2017. Therefore, DoD doesn’t consider NIST SP 800-171 compliance technologies or documentation a new expense.
The good news is that there is CMMC compliance software available that can significantly reduce the time and cost of achieving compliance, like PreVeil.
How to Get CMMC Certified: 3 Steps to Get Started
If you’re just starting your journey to becoming CMMC compliant, you should focus on meeting the 110 controls in NIST 800-171. PreVeil is a company that assists with CMMC Level 2 readiness and offers a three-step roadmap to CMMC compliance.
1. Adopt a proven platform for storing, processing and transmitting CUI.
You’ll need to choose an email and file sharing platform that complies with DFARS 7012. Know that common commercial email solutions like Gmail and Microsoft O365 are not compliant & the responsibility for choosing a compliant platform rests squarely on the shoulders of defense contractors; Ask for evidence that customers have achieved CMMC compliance with a given solution.
Over 50 PreVeil customers have achieved CMMC compliance- validated by a perfect 110 score. PreVeil is used by thousands of defense contractors and through a combination of inherited and shared controls, PreVeil supports over 90% of the NIST 800-171 security controls (102 of the 110).
2. Use pre-filled documentation to save time and money.
Defense contractors have to do more than implement technology and policies to comply with NIST SP 800-171. They also need detailed, evidence-based documentation to prove it. This can be a daunting, time-consuming, and costly task.
PreVeil offers its customers a Compliance Accelerator documentation package that gives them a huge head start. It includes a pre-filled System Security Plan (SSP) with detailed language that explains how a customer will be able to meet each of the NIST SP 800-171 controls and objectives that PreVeil supports; policy documents; POA&M templates and more. Here’s what Paul Miller from Virtra said:
I would say the Preveil supporting documentation halved our time that we spent on the SSP. The pre-filled documents gave us that starting place to make sure we addressed everything in each control.
3. Identify certified consultants that are familiar with your technology
It’s understandable that many organizations lack the internal security expertise to conduct their NIST 800-171 self-assessment accurately. If you get stuck, partners can save you time and money.
For this reason, PreVeil has built a Preferred Partner Network of C3PAOs, Consultants, and MSPs, all with expert knowledge of DFARS, NIST, CMMC and PreVeil.
CMMC is already entering contracts, so if you’re behind, PreVeil can help you catch up.
CMMC Compliance FAQs
Does CMMC require FedRAMP?
If contractors use a cloud service provider (CSP) to handle Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), that provider must meet FedRAMP Moderate baseline or equivalent in order to meet CMMC compliance requirements. PreVeil meets these FedRAMP requirements.
How long does it take to get a CMMC certification?
The timeline varies based on scope, resources, and readiness. For most organizations, achieving CMMC certification will take 6–12 months, depending on the current state of compliance and remediation needs.
How many CMMC controls are there?
CMMC is aligned with NIST SP 800-171 and includes 110 security controls at Level 2, plus additional enhanced controls at Level 3.
Who created CMMC?
The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD), now known as the Department of War, developed CMMC to strengthen the protection of sensitive government data (CUI) across the defense industrial base (DIB).
Does CMMC require GCC High?
No. While GCC High is one option to protect CUI, it can be expensive, complex to manage, and disruptive to existing workflows. PreVeil offers a cost-effective and easy-to-deploy alternative that meets CMMC compliance requirements without forcing organizations to migrate their entire IT environment. With end-to-end encrypted email and file sharing, seamless integration with Outlook, Gmail, and mobile devices, and strong security aligned with NIST 800-171, PreVeil enables contractors to achieve compliance faster and at a lower cost than GCC High.
To Learn More about CMMC Compliance
PreVeil is trusted by more than 2,000 small and midsize defense contractors. Learn more about how PreVeil’s proven solution can help you achieve CMMC Level 2 certification faster and more affordably: